How to bypass security when adding UI to Gmail App from Chrome Extension
Gmail is very strict about what you can do with their UI. They have a lot of security measures to prevent you from doing anything that might harm their users. So, how bypass these measures and carry on doing what you want (or are required) to do anyway?
In this article, we will be trying to solve 2 problems:
- Gmail does not allow to reassign
innerHTML.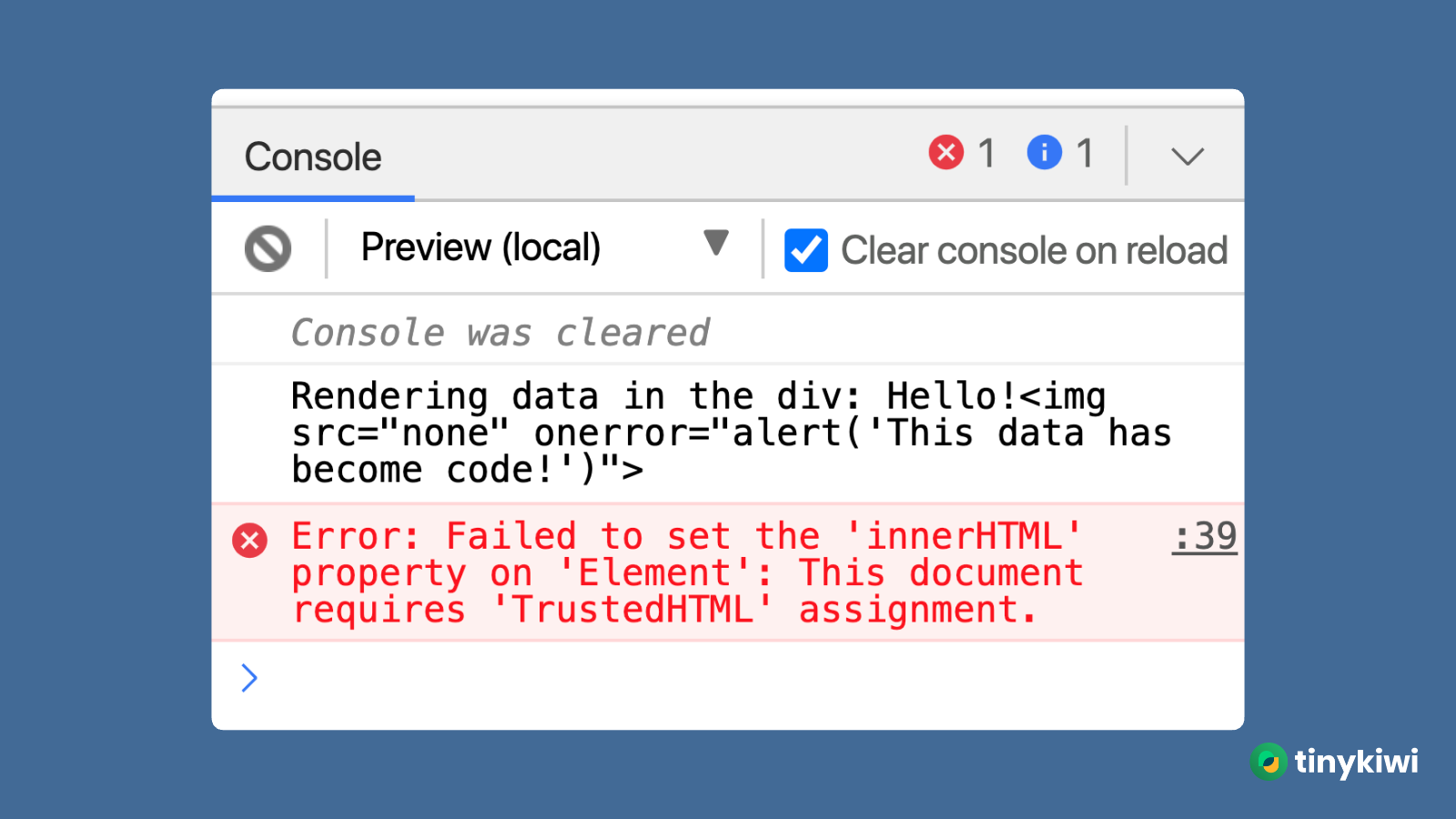
- Gmail does not allow to create new
Workerservice.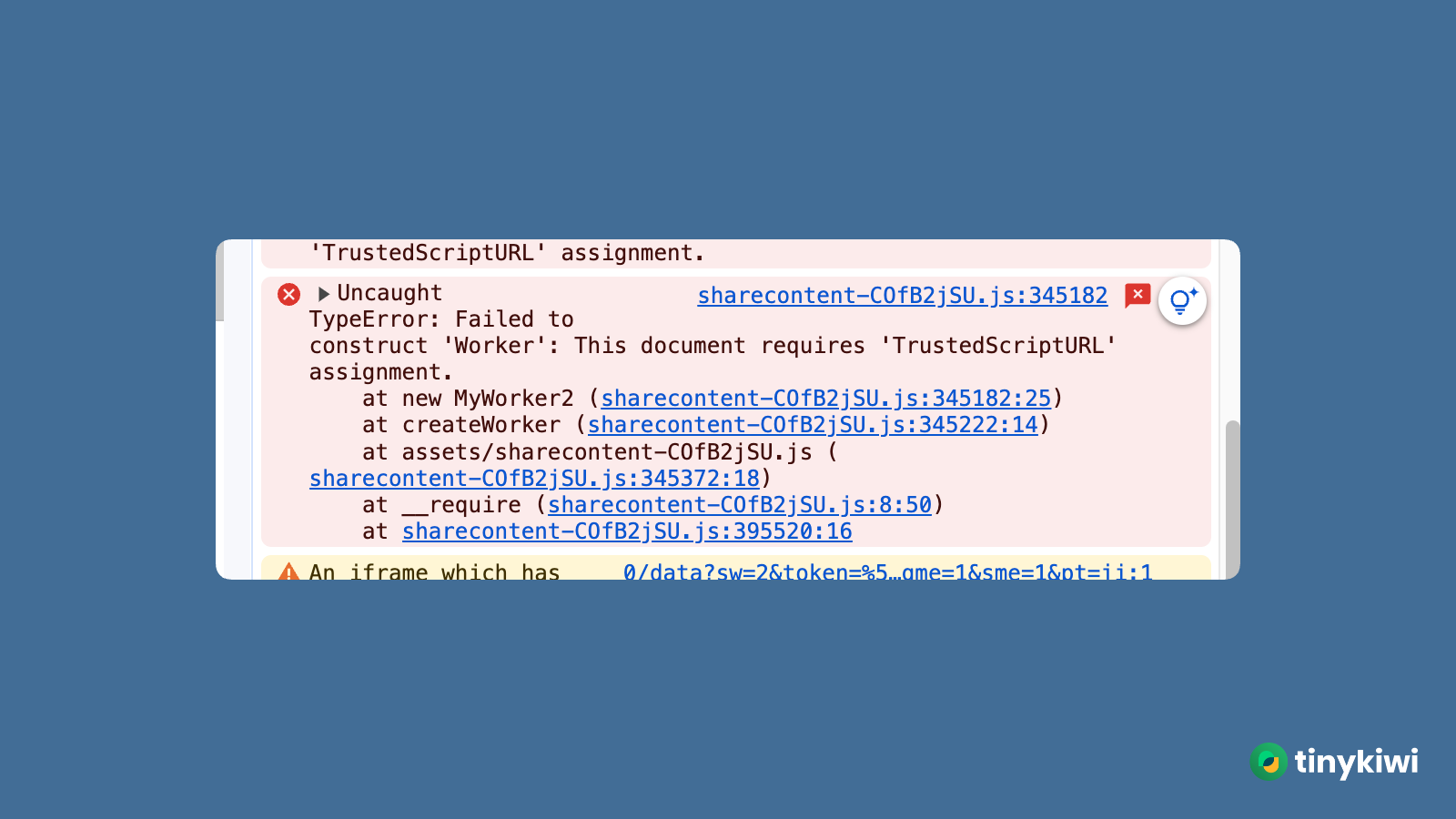
Personal context: I am trying to make an extension that use AntD design components and under the hood they use all kind of operations that require trusted policies like assigning innerHTML, create new Worker service and so on. Apparently Gmail won’t allow you to do it easily. But it does not mean that is impossible. Let’s see how we can solve these problems.
Gmail does not allow to reassign innerHTML
The root cause: Gmail only allow Trusted Types to be assigned to innerHTML. Trusted Types is a new security feature that helps prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks by enforcing a strong policy for the types of values that can be assigned to certain properties, like innerHTML. You can read more about it here: https://web.dev/trusted-types/. Event when you does not intentionally use it, the vendor’s logic included in the script you injected on Gmail UI load might use the innerHTML assignment.
How to solve it:
- Create a custom ‘default’ policy that allow you to assign
innerHTMLto the element you want
// csp/trusted-security-policies.js
if (window.trustedTypes && window.trustedTypes.createPolicy) {
window.trustedTypes.createPolicy("default", {
createHTML: (string) => string,
createScriptURL: (string) => string,
createScript: (string) => string,
});
}
- Load them before calling the main logic of the your web resources.
const trustedPolicyScript = document.createElement("script"); trustedPolicyScript.src = chrome.runtime.getURL( "csp/trusted-security-policies.js" ); trustedPolicyScript.onload = function () { trustedPolicyScript.remove(); // Call the main logic of your web resources here }; document.body.appendChild(trustedPolicyScript);
Gmail does not allow to create new Worker service.
The root cause: Gmail’s response to load the page include the Content-Security-Policy header specify which script-src is allowed to load. The Worker service that your script is trying to call is very likely not in the list of allowed sources.
How to solve it:
- Chrome Extension provide the ability to remove header of response before it is processed by the browser. You can use this ability to remove the
Content-Security-Policyheader from Gmail’s response. You can read more aboutdeclarativeNetRequesthere: https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/reference/declarativeNetRequest/
chrome.runtime.onInstalled.addListener(async (details) => {
const dynamicRule = {
id: 1,
priority: 1,
condition: {
urlFilter: "https://mail.google.com/mail/u/0/",
//* if CSP get thrown again, try whitelist all resource type to catch the first request
//* whatever type it is the url has to be exact match
resourceTypes: ["main_frame", "sub_frame", "xmlhttprequest"],
},
action: {
type: "modifyHeaders",
responseHeaders: [
{
header: "Content-Security-Policy",
operation: "remove",
},
{
header: "X-Content-Security-Policy",
operation: "remove",
},
],
},
};
chrome.declarativeNetRequest.updateDynamicRules({
removeRuleIds: [1],
addRules: [dynamicRule],
});
});
 Phat Or Nemo
Phat Or Nemo